Vascular and Vein Surgery
What is carotid artery disease?
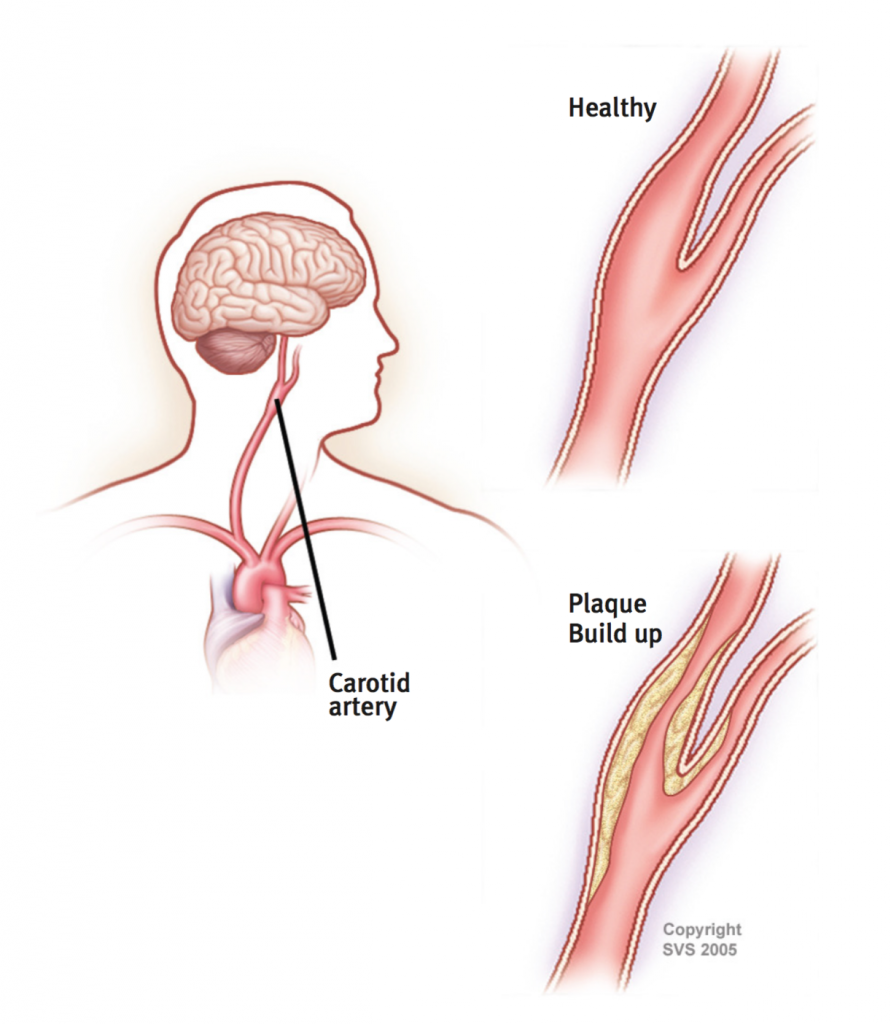
Your arteries are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood from your heart to other parts of your body. Your carotid arteries are two main arteries that carry blood from your heart, up through your neck, to your brain. Healthy carotid arteries are smooth and unobstructed, allowing blood to flow freely to the brain and provide oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients that your brain cells need. Typically with age, the carotid arteries build up plaque,
a sticky substance made up mostly of fat and cholesterol. Plaque narrows the passageway within the arteries and causes them to become stiff. Carotid artery disease results when the carotid arteries become too narrow or obstructed
and limit the blood flow to the brain.
Strokes result either from obstruction of blood flow to the brain by the plaque or when bits of plaque and clots break off from the plaque and flow to the brain. If left untreated, carotid artery disease may lead to stroke, where lack of oxygen and other essential nutrients cause damage to the brain. Depending on its severity, a stroke can be fatal. In fact, strokes are the third leading cause of death in the United States and the leading cause of permanent disability in older adults.
Causes and risk factors
• Age
• Hypertension (high blood pressure)
• Diabetes
•Smoking
• High cholesterol
• Obesity
• Lack of exercise
• Family history of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and/or stroke
• Irregular heartbeat, particularly atrial fibrillation (a diagnosed condition where the heart chambers quiver and beat ineffectively)
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms in the early stages of carotid artery disease, and stroke could be the first sign of the condition. Stroke, however, typically has warning signs, referred to as ministrokes or transient ischemic attacks. Ministroke symptoms are usually temporary, lasting a few minutes to a few hours, and should be treated as serious medical emergencies requiring immediate treatment because they are strong predictors of future stoke.
Some symptoms of stroke include:
• Weakness, numbness, or tingling on one side of the body
• Inability to control movement of a body part
• Loss of vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes
• Inability to speak clearly
• Difficulty talking or comprehending what others are saying
• Dizziness or confusion
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of carotid artery disease can be confirmed, and its severity established,by a noninvasive Duplex ultrasound examination. If you experience symptoms of a 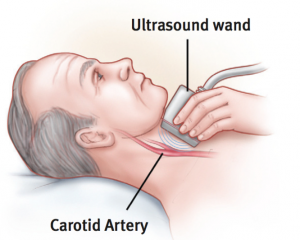
 ministroke (as described above), see a vascular surgeon. They are the only physicians treating vascular disease today who can perform all the treatment options available, including medical management, minimally invasive endovascular angioplasty and stent procedures, and carotid endarterectomy. Only when you see a vascular surgeon who offers all treatment modalities will you be assured of receiving the care that is most appropriate to your condition.
ministroke (as described above), see a vascular surgeon. They are the only physicians treating vascular disease today who can perform all the treatment options available, including medical management, minimally invasive endovascular angioplasty and stent procedures, and carotid endarterectomy. Only when you see a vascular surgeon who offers all treatment modalities will you be assured of receiving the care that is most appropriate to your condition.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of your condition, treatment options may include lifestyle changes, medications, or a definitive procedure such as Transcarotid Artery Revascularization (TCAR), minimally invasive carotid stenting, and open carotid endarterectomy.
Vascular surgeons are the only physicians treating vascular disease today who can perform all treatment options available, including medical management, minimally invasive endovascular procedures including balloon angioplasty, atherectomy, and stent procedures, and open surgical repair including bypass.

